
We can confirm the installation using both the command line and graphical user interface. When the packages are installed, the application will be available on your system.
#Install gedit linux password#
$ sudo apt updateĮnter your password and do not make a mistake while entering it.
#Install gedit linux install#
Check the following commands and they will help you to install the software.
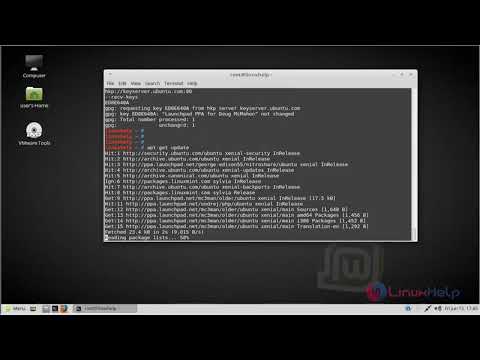
This helps us to install an up to date software.
#Install gedit linux update#
Install gEdit on Ubuntu 20.04 LTSįirst, we update the repositories available on our system. The gEdit text editor does not require any prerequisites. The text editor has an enormous number of functions and can be used for programming purposes as well. I am using Ubuntu 20.04 Mate edition, and it does not come preinstalled. It is developed by Gnome and can be installed from standard Ubuntu repositories.

You won’t need to do this when you are editing your own files.There are several text editors available for Linux and one of them is gEdit. This step is purely for demonstration purposes to make sure the new file does not have the same mode permissions and ownership as the original file. To ensure we have a change of file ownership and mode permissions, we’ll create a new file and then copy the existing file over it. Let’s say we want to edit the fstab file. You need to make sure these are exactly the same on your new file as they are on the original file before you copy the new version over the original file. When you copy a file, the file ownership can change, and the file mode permissions can be altered. If you make a mess of editing the copied file, there’s no harm done. When you’ve finished editing the new file, you can copy it back over the original file. Replicating Ownership and Permissions to a New FIleĪ cautious way to edit system files–and therefore a commendable way to edit system files-is to copy the file and then edit the copy. This command opens gedit and loads the samba config file for editing. You get the command line prompt back straight away and you can carry on using the terminal window even when gedit is running. If you want to use the terminal window while gedit is still open, launch gedit with this command instead. The terminal window will wait for gedit to close before it returns you to the command prompt. It’s often named “Text Editor.” Just search the applications menu for “gedit.” Of course, you can also launch gedit from your Linux desktop’s application menu. You can get on with the task of typing up whatever you’re working on with no distractions. It’s an uncluttered and clean application window. The gedit text editor will appear shortly. To start gedit from the command line, type gedit and hit Enter. RELATED: What Does "Everything Is a File" Mean in Linux? Launching gedit It’s a handy tool for editing files when all you need is just enough editor to get the job done-without the learning curve of some of the power-house editors like vim. That includes Ubuntu, Fedora, Debian, CentOS, and Red Hat. The default GNOME text editor is gedit, so you should find it on any system with a GNOME desktop environment.
You can read these files to learn more about the inner workings of your operating system, and you can edit them to change its behavior. While that’s not strictly accurate, text files are often used for system logs and configuration.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
